Physical Activity and Supportive Care Intervention Preferences: A Cross-Sectional Study of Barriers in Advanced Cancer
Abstract
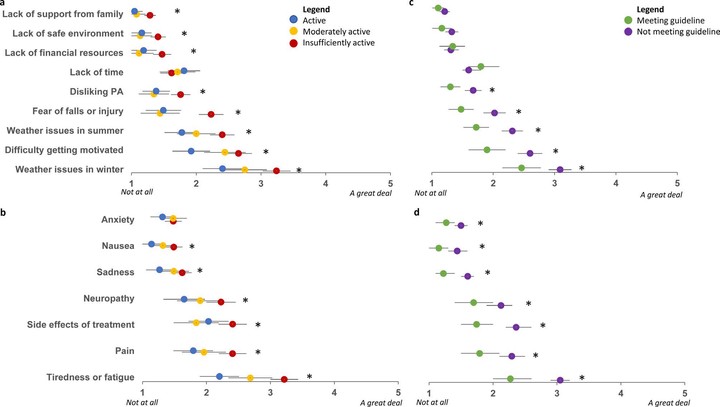
Purpose Physical activity may greatly benefit adults living with advanced cancer; however, barriers to physical activity and preferences for supportive care interventions are not well understood. This study investigates barriers to physical activity and differences in intervention preferences by demographic and clinical characteristics among adults with advanced cancer. Methods Data came from a cross-sectional study of 247 adults with advanced cancer who visited the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Centre from January 2021 to January 2023. The Godin–Shepard Leisure Score Index (insufficiently active, moderately active and active) was used to assess physical activity. Physical activity barriers were reported as mean scores (1–5: ‘not at all’ to ‘a great deal’). Differences in intervention preferences were assessed using X2 tests. Results Adults living with advanced cancer were insufficiently active (53%), moderately active (21%) or active (26%). Respondents identified several barriers to physical activity spanning tiredness (x̄=3.2), winter weather concerns (x̄=3.2) and lack of motivation (x̄=2.7). Respondents were most interested in a supportive care intervention designed to increase energy (88%) and improve physical health (86%) with physical therapy (73%), walking (72%) and resistance exercises (72%). Differences in preferences emerged by demographic characteristics and to a lesser extent by clinical characteristics. Conclusions Adults with advanced cancer reported several barriers to physical activity. Future interventions should emphasise increasing energy and physical health and include strategies to manage tiredness and winter weather concerns.