The Age-Related Eye Disease Study severity scale for age-related macular degeneration: AREDS Report No. 17
Abstract
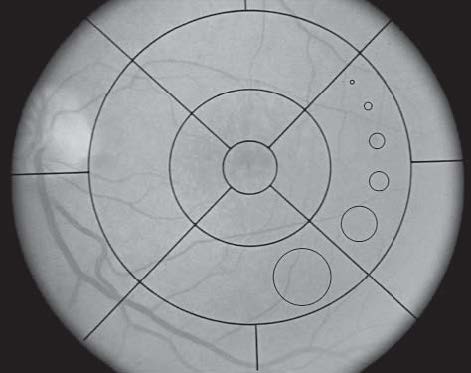
OBJECTIVE: To develop a fundus photographic severity scale for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). METHODS: In the Age-Related Eye Disease Study, stereoscopic color fundus photographs were taken at baseline, at the 2-year follow-up visit, and annually thereafter. Photographs were graded for drusen characteristics (size, type, area), pigmentary abnormalities (increased pigment, depigmentation, geographic atrophy), and presence of abnormalities characteristic of neovascular AMD (retinal pigment epithelial detachment, serous or hemorrhagic sensory retinal detachment, subretinal or sub-retinal pigment epithelial hemorrhage, subretinal fibrous tissue). Advanced AMD was defined as presence of 1 or more neovascular AMD abnormalities, photocoagulation for AMD, or geographic atrophy involving the center of the macula. We explored associations among right eyes of 3212 participants between severity of drusen characteristics and pigmentary abnormalities at baseline and development of advanced AMD within 5 years of follow-up. RESULTS: A 9-step severity scale that combines a 6-step drusen area scale with a 5-step pigmentary abnormality scale was developed, on which the 5-year risk of advanced AMD increased progressively from less than 1% in step 1 to about 50% in step 9. Among the 334 eyes that had at least a 3-step progression on the scale between the baseline and 5-year visits, almost half showed stepwise progression through intervening severity levels at intervening visits. Replicate gradings showed agreement within 1 step on the scale in 87% of eyes. CONCLUSIONS: The scale provides convenient risk categories and has acceptable reproducibility. Progression along it may prove to be useful as a surrogate for progression to advanced AMD.