Abstract
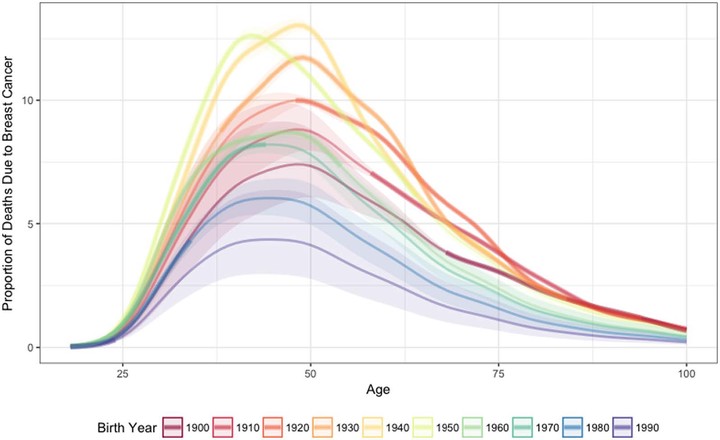
OBJECTIVE: Breast cancer simulation models must take changing mortality rates into account to evaluate the potential impact of cancer control interventions. We estimated mortality rates due to breast cancer and all other causes combined to determine their impact on overall mortality by year, age, and birth cohort. METHODS: Based on mortality rates from publicly available datasets, an age-period-cohort model was used to estimate the proportion of deaths due to breast cancer for US women aged 0 to 119 years, with birth years 1900 to 2000. Breast cancer mortality was calculated as all-cause mortality multiplied by the proportion of deaths due to breast cancer; other-cause mortality was the difference between all-cause and breast cancer mortality. RESULTS: Breast cancer and other-cause mortality rates were higher for older ages and birth cohorts. The percent of deaths due to breast cancer increased across birth cohorts from 1900 to 1940 then decreased. Among 50-year-old women, in the 1920 birth cohort, 52 (9.9%) of 100,000 deaths (95% CI, 9.8% to 10.1%) were attributed to breast cancer whereas 476 of 100,000 were due to other causes; in the 1960 birth cohort, 22 (8.5%) of 100,000 deaths (95% CI, 8.3% to 8.7%) were attributed to breast cancer with 242 of 100,000 deaths due to other causes. The percentage of all deaths due to breast cancer was highest (4.1% to 12.9%) for women in their 40s and 50s for all birth cohorts. CONCLUSIONS: This study offers evidence that advances in breast cancer screening and treatment have reduced breast cancer mortality for women across the age spectrum, and provides estimates of age-, year- and birth cohort-specific competing mortality rates for simulation models. Other-cause mortality estimates are important in these models because most women die from causes other than breast cancer.