Feasibility and Acceptability of Home-Based Strength Training in Endometrial Cancer Survivors
Abstract
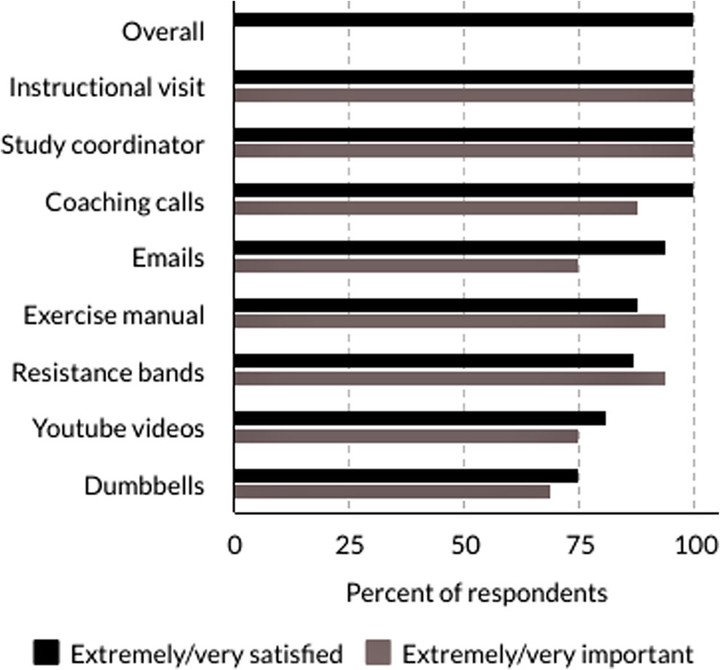
Purpose Physical activity is important for healthy cancer survivorship, yet many endometrial cancer survivors do not participate in recommended muscle-strengthening activity. The purpose of this study was to determine the feasibility of home-based muscle strengthening activity in endometrial cancer survivors. Methods Forty post-treatment endometrial cancer survivors were enrolled in a randomized trial, of twice-weekly home-based strength exercise versus wait-list control. The intervention included educational materials, exercise equipment (dumbbells, resistance bands), and support/feedback via video coaching sessions. Participants completed the exercises twice per week for 10 weeks, with a 5-week follow-up period. Feasibility was measured by program adherence, as well as safety of and satisfaction with the study. Results On average, participants were 60.9 years old (SD = 8.7), had a BMI of 39.9 kg/m2 (SD = 15.2), and were 2.9 years (SD = 1.2) since diagnosis. The majority (83%) had stage I disease at diagnosis. Seventy-five percent adhered to the exercise prescription of twice/week, with 85% of participants missing fewer than 3 of the workouts. Forty percent of participants continued workouts during the 5-week follow-up. Participants were highly satisfied with intervention. No injuries or adverse everts occurred. Conclusion This home-based program was feasible in endometrial cancer survivors. While adherence was measured, future research should focus on long-term maintenance of exercise and should explore progressions and modifications of exercises at a distance for various abilities. Implications for Cancer Survivors Muscle strengthening activities are recommended for all cancer survivors. This study shows that a home-based muscle strengthening exercise is feasible in endometrial cancer survivors.