Use of the lowest vertebral body T-score to diagnose lumbar osteoporosis in men: is "cherry picking" appropriate?
Abstract
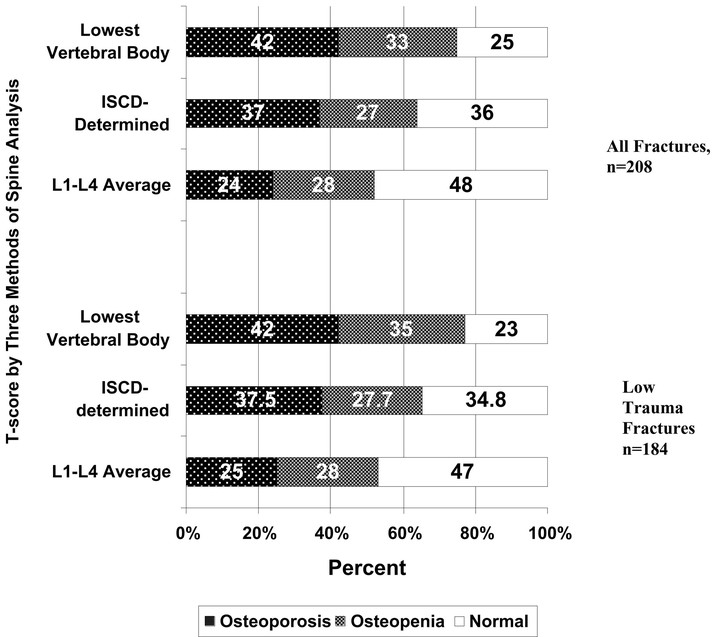
In this study, we hypothesized that use of the lowest T-score among four lumbar vertebral bodies would lessen the impact of degenerative arthritis and other artifacts on diagnostic categorization at this site and increase study sensitivity, classifying more men with prior fracture as osteoporotic than the other two methods of lumbar spine analysis. Bone density studies of 533 male veterans measured between January and October 2002 were reviewed to determine diagnostic classification using the L1-L4 average, International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD)-determined, and lowest lumbar vertebral body T-score. We calculated sensitivity and specificity of the three methods of spine analysis, using spine osteoporosis to indicate a positive test and prior fracture as the true indicator of osteoporosis. The lowest lumbar T-score performed with similar sensitivity and specificity to that of the lowest hip or wrist T-score in the ability to classify men with prior fracture as osteoporotic, whereas the average L1-L4 and ISCD-determined T-scores performed with lower sensitivity, but better specificity. In conclusion, this retrospective study suggests that use of the lowest vertebral body T-score among men increases diagnostic sensitivity of lumbar spine bone mass measurement. Prospective studies are needed to determine which of these three methods of lumbar spine analysis best predicts future fragility fracture in men and women.