Esophageal clearance patterns in normal older adults as documented with videofluoroscopic esophagram
Abstract
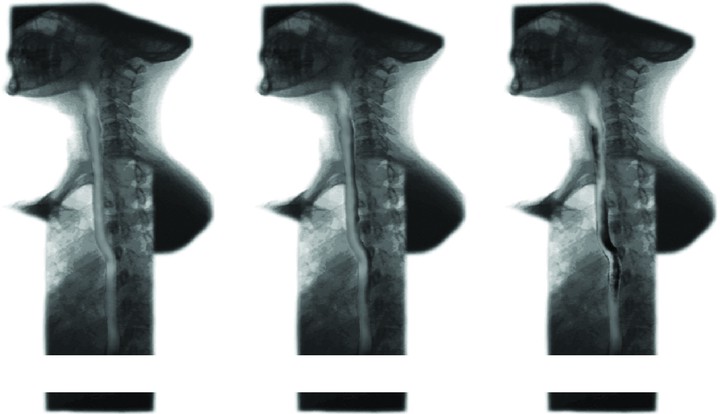
Normal esophageal bolus transport in asymptomatic healthy older adults has not been well defined, potentially leading to ambiguity in differentiating esophageal swallowing patterns of dysphagic and healthy individuals. This pilot study of 24 young (45-64 years) and old (65+years) men and women was designed to assess radiographic esophageal bolus movement patterns in healthy adults using videofluoroscopic recording. Healthy, asymptomatic adults underwent videofluoroscopic esophagram to evaluate for the presence of ineffective esophageal clearance, namely, intraesophageal stasis and intraesophageal reflux. Intraesophageal stasis and intraesophageal reflux were visualized radiographically in these normal subjects. Intraesophageal stasis occurred significantly more frequently with semisolid (96%) compared with liquid (16%) barium, suggesting that a variety of barium consistencies, as opposed to only the traditional fluids, would better define the spectrum of esophageal transport. Intraesophageal reflux was observed more frequently in older males than in their younger counterparts. The rates of intraesophageal stasis and intraesophageal reflux were potentially high given that successive bolus presentations were spaced 10 seconds apart. These findings suggest a need for a more comprehensive definition regarding the range of normal esophageal bolus transport to (a) prevent misdiagnosis of dysphagia and (b) to enhance generalization to functional eating, which involves solid foods in addition to liquids.