Skin Intrinsic Fluorescence and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The Beaver Dam Eye Study
Abstract
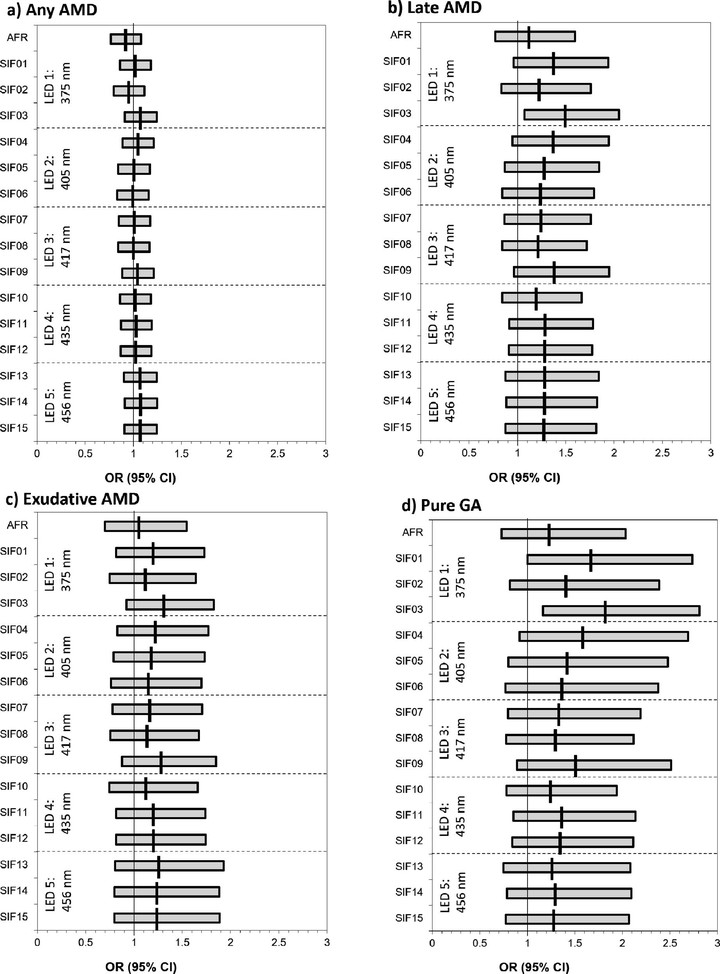
Purpose: To determine if skin intrinsic fluorescence (SIF), a noninvasive measure of advanced glycation endproducts and oxidative stress in skin is associated with AMD. Methods: SIF was measured with the SCOUT DS skin fluorescence spectrometer in a cross-sectional cohort study of 969 persons aged 68 to 102 years from the 1181 who participated in the 25-year follow-up examination in the Beaver Dam Eye Study (BDES) in 2014 to 2016. The SCOUT DS skin fluorescence spectrometer uses five light-emitting diodes, centered at 375 nm to 456 nm. AMD was assessed by grading of digital color 45° stereoscopic fundus photographs of the macula using the Wisconsin Age-Related Maculopathy grading scheme. Analyses included logistic regression with generalized estimating equations to account for correlation between the eyes of a person. Results: There were data for 1827 eyes for analyses. Early AMD was present in 22% and late AMD in 4% of the eyes. While adjusting for age, sex, smoking status, and history of cardiovascular disease, there were no significant associations of any SIF measure with any AMD or exudative AMD. SIF01 (odds ratio per 1 SD difference on the log scale, 95% confidence interval) (1.66, 1.00-2.74, P = 0.05) and SIF03 (1.81, 1.16-2.81, P = 0.008) were associated with geographic atrophy. Conclusions: There was a suggestive relationship of two SIF measures, SIF01 and SIF03, using different correction factors from the excitation centered at 375 nm, with the prevalence of geographic atrophy in the BDES. Longitudinal follow-up is indicated to assess a temporal relationship.