Abstract
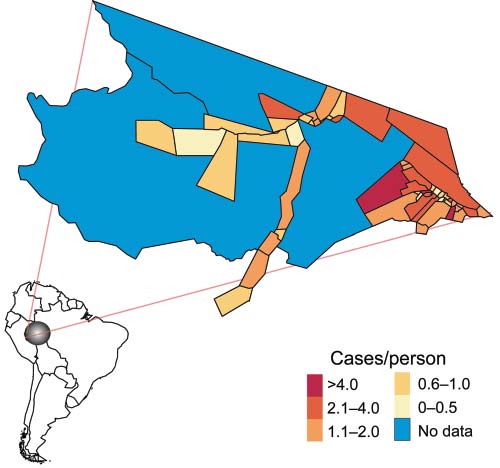
Malaria is the most prevalent vector-borne disease in the Amazon. We used malaria reports for health districts collected in 2006 by the Programa Nacional de Controle da Malaria to determine whether deforestation is associated with malaria incidence in the county (municipio) of Mancio Lima, Acre State, Brazil. Cumulative percent deforestation was calculated for the spatial catchment area of each health district by using 60 x 60-meter, resolution-classified imagery. Statistical associations were identified with univariate and multivariate general additive negative binomial models adjusted for spatial effects. Our cross-sectional study shows malaria incidence across health districts in 2006 is positively associated with greater changes in percentage of cumulative deforestation within respective health districts. After adjusting for access to care, health district size, and spatial trends, we show that a 4.2%, or 1 SD, change in deforestation from August 1997 through August 2001 is associated with a 48% increase of malaria incidence.