Abstract
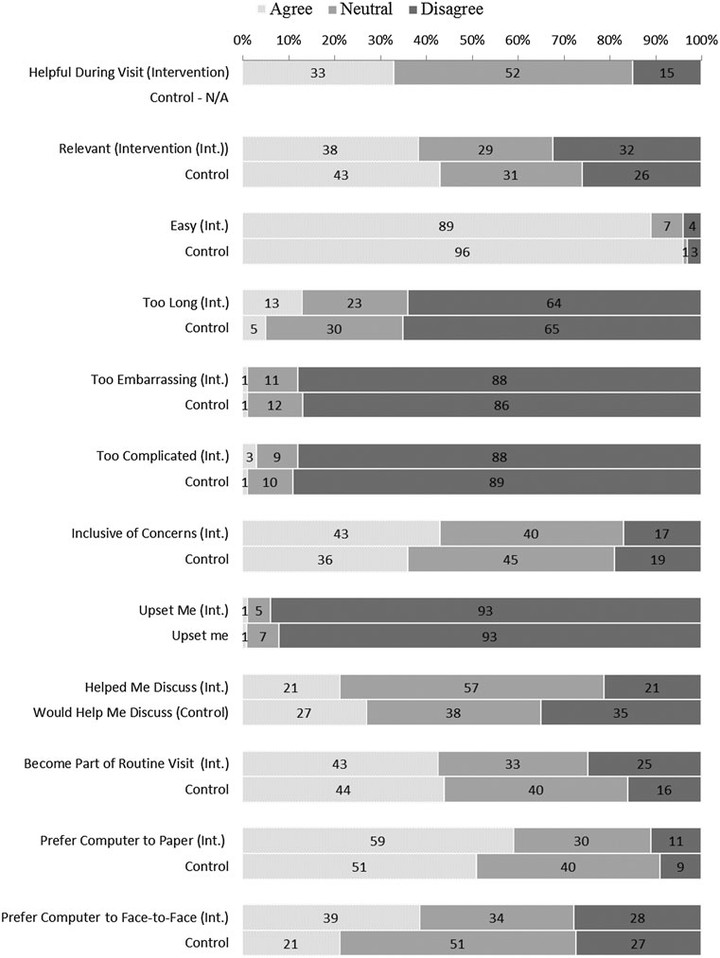
BACKGROUND: A minority of women with urinary incontinence (UI) and even fewer with fecal incontinence (FI) report having discussed it with a health care provider in the past year. Thus our aim was to evaluate whether the use of an electronic pelvic floor assessment questionnaire (ePAQ-PF) improves communication about incontinence in primary care. METHODS: Women 40 years and older who were scheduled for an annual wellness physical at an internal medicine clinic between August 2007 and August 2008 were randomized to complete the ePAQ-PF prior to (n = 145) or after (n = 139) their visit. Clinicians of women in the intervention group received the ePAQ-PF report prior to the visit. Outcome measures from clinic note abstraction included mention of UI (primary) and FI. Participant-reported outcome measures included discussion of UI and FI and initiator of discussion. RESULTS: Discussions of UI was more common in the intervention group than the control group: (27% vs. 19%; odds ratio [OR], 1.6 95% confidence interval [95%CI] 0.9-2.8, particularly for women over 60 (33% vs. 12%; OR 3.8, 95%CI 1.2-11.8) and for women with UI (42% vs. 25%; OR 2.2, 95%CI 1.1-4.1). The intervention primarily led to an increase in clinician-initiated UI discussions which were more common in the intervention group (18% vs. 4%, OR 4.8, 95%CI 1.9-12.0) Participants in the intervention group more frequently reported discussion of FI (14% vs. 6%; OR 2.5, 95%CI 1.1-6.0) which was clinician initiated in over half the cases (9% vs. 3%; OR 3.5, 95%CI 1.1-11.0). CONCLUSIONS: Use of the ePAQ-PF prior to clinic visits increases discussion of UI and FI, particularly clinician-initiated discussion. These findings suggest that such instruments may increase the detection and treatment of this often ‘silent’ affliction.