Abstract
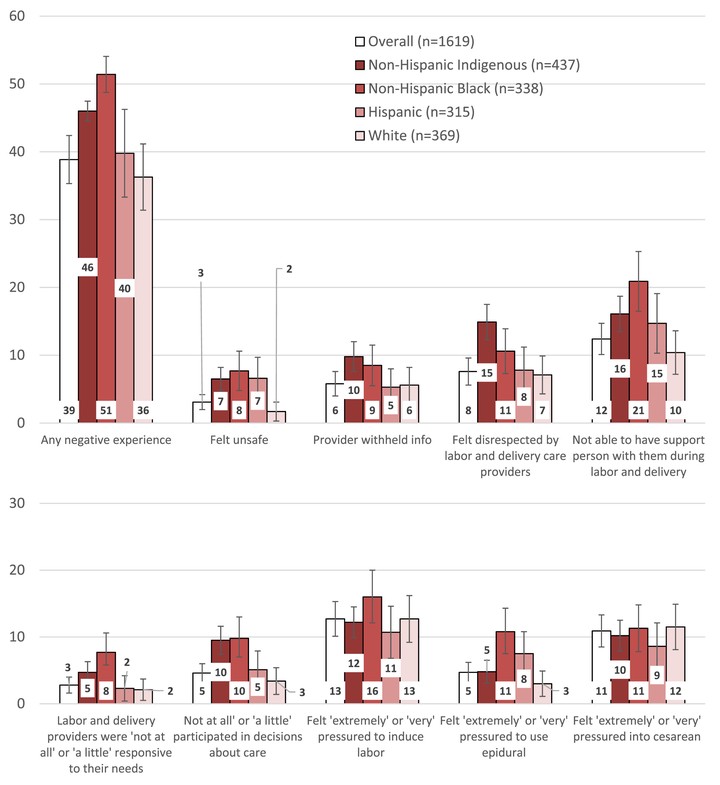
Policymakers and researchers have posited intrapartum care as a potential mediator of racial inequities in perinatal outcomes. However, few studies have measured patient-centered quality of intrapartum care or explored differences by race. To address this gap, we developed a survey supplement using cognitive interviewing and administered it to a probability-based race-stratified random sample of people who recently gave birth in Wisconsin in 2020, including oversamples of non-Hispanic Black and Indigenous birthing people. We estimate overall and race-specific prevalences of intrapartum care experiences and use survey-weighted mixed effects ordinal and logistic regression to estimate differences in intrapartum care experiences by race/ethnicity and hospital characteristics. We find significant racial differences in the population prevalence of negative experiences of intrapartum care providers, including disrespect, lack of responsiveness, inclusion in decision-making about care, and pressure to use epidural analgesia. In unadjusted models, both non-Hispanic Indigenous (American Indian/Alaska Native) and non-Hispanic Black respondents had higher odds (than non-Hispanic White birthing people) of reporting several negative intrapartum experiences, including feeling disrespected by providers and experiencing a lower level of care team responsiveness. In adjusted models, Indigenous respondents had significantly higher odds of reporting that intrapartum care providers withheld information, showed disrespect, and were less responsive. Giving birth at a low birth-volume hospital was associated with higher odds of reporting greater participation in decision-making.