Abstract
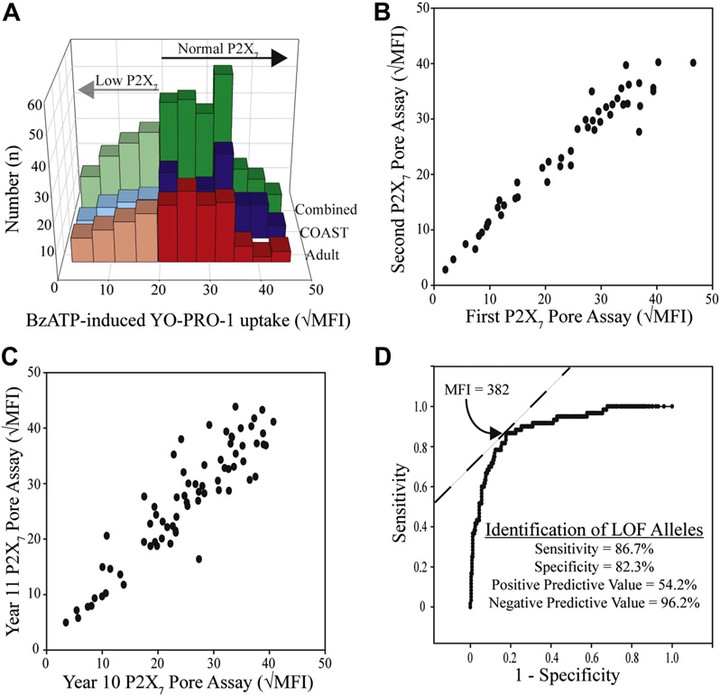
BACKGROUND: Viral illnesses are important factors in both asthma inception and exacerbations, and allergic sensitization in early life further enhances asthma risk through unclear mechanisms. Cellular damage caused by infection or allergen inhalation increases ATP levels in the airways with subsequent purinergic receptor activation. The purinergic receptor P2X(7) can enhance airway leukocyte recruitment to the airways, and P2X(7) knockout mice display a reduced asthma-like phenotype. OBJECTIVE: Based on the P2X(7) knockout mouse, we hypothesized that children with low P2X(7) function would have decreased rates of asthma. METHODS: We used a functional assay to determine P2X(7) pore-producing capacity in whole-blood samples in a birth cohort at high risk for asthma development. The P2X(7) assay was validated with known loss-of-function alleles in human subjects. P2X(7) pore status categorization was used to assess asthma and allergy status in the cohort. RESULTS: Attenuated P2X(7) function was associated with lower asthma rates at ages 6 and 8 years, and the greatest effects were observed in boys. Children with asthma at age 11 years who had low P2X(7) capacity had less severe disease in the previous year. Attenuated P2X(7) function was also associated with sensitization to fewer aeroallergens. CONCLUSION: P2X(7) functional capacity is associated with asthma risk or disease severity, and these relationships appear to be age related.